three phase alternating current
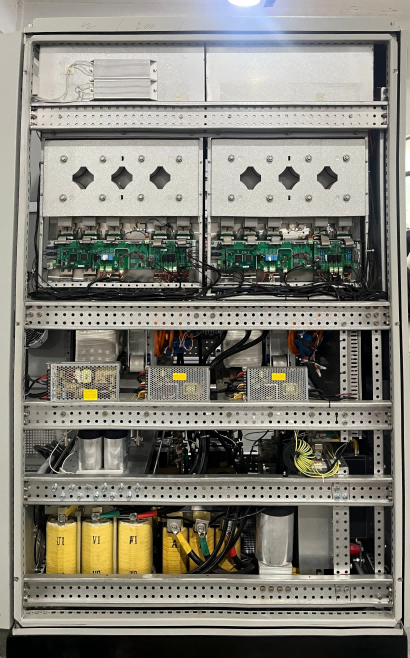
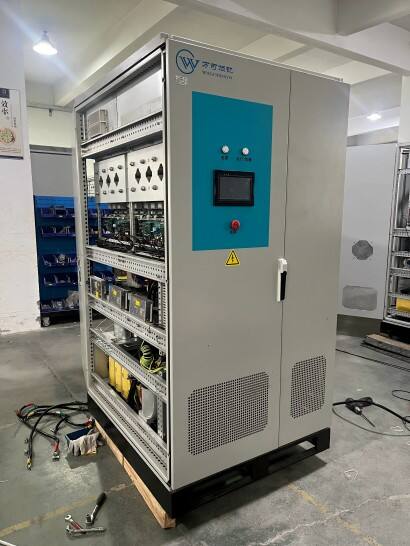
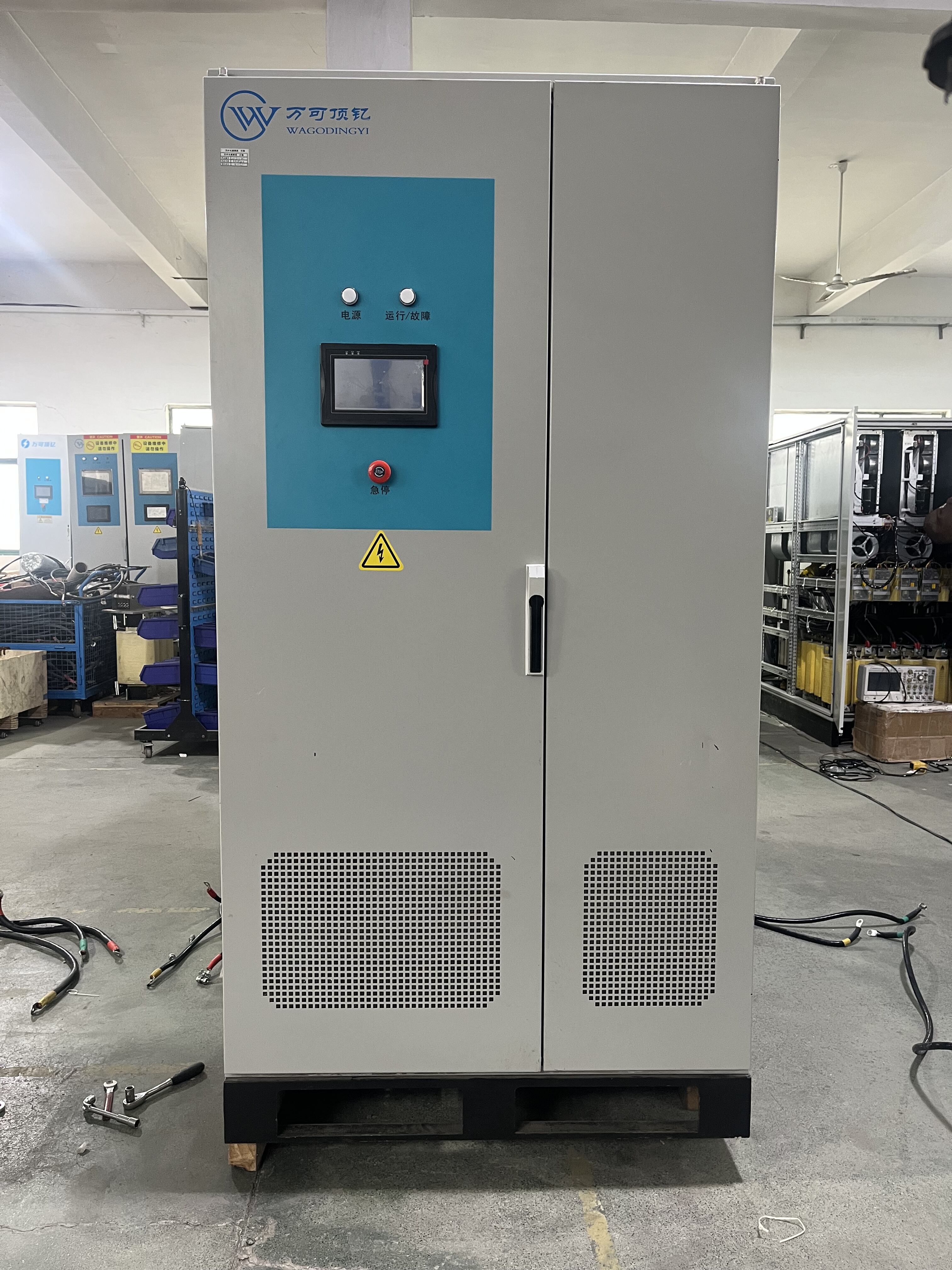
Three phase alternating current (AC) represents a sophisticated power distribution system that generates, transmits, and delivers electrical power through three separate phases. This system, operating at a phase difference of 120 degrees between each conductor, provides a more efficient and reliable power solution compared to single phase systems. The fundamental principle involves three separate conductors carrying alternating currents of the same frequency and voltage amplitude, but with different phase angles. This configuration creates a rotating magnetic field that enables the smooth operation of electric motors and other industrial equipment. Three phase AC power is particularly notable for its constant power delivery, minimal voltage drop, and superior power factor characteristics. In industrial applications, it powers heavy machinery, manufacturing equipment, and large HVAC systems. Commercial buildings rely on three phase power for elevators, data centers, and comprehensive electrical installations. The system's inherent efficiency makes it ideal for power transmission over long distances, with minimal power losses and reduced conductor material requirements. Modern smart grid systems utilize three phase AC as their backbone, enabling sophisticated power management and distribution across vast networks. The technology's reliability and scalability have made it the standard choice for industrial power distribution worldwide, supporting everything from small manufacturing operations to massive industrial complexes.